What is a Battery?
Published: December 14, 2023
A battery is defined as any device delivering electrical energy generated by direct conversion of chemical energy.
When a chemical reaction generates electricity, it can be either reversible or irreversible. If the reaction is irreversible, the battery is called a "primary battery" and is disposed of once all the chemical energy is converted to electricity. If the reaction is reversible, the battery is referred to as a "secondary battery,” which is more commonly known as a rechargeable battery. Rechargeable batteries can be recharged by adding electricity and used repeatedly, which is why they are also known as accumulators.
Due to the wide range of applications, the category of portable batteries can be further divided as follows:
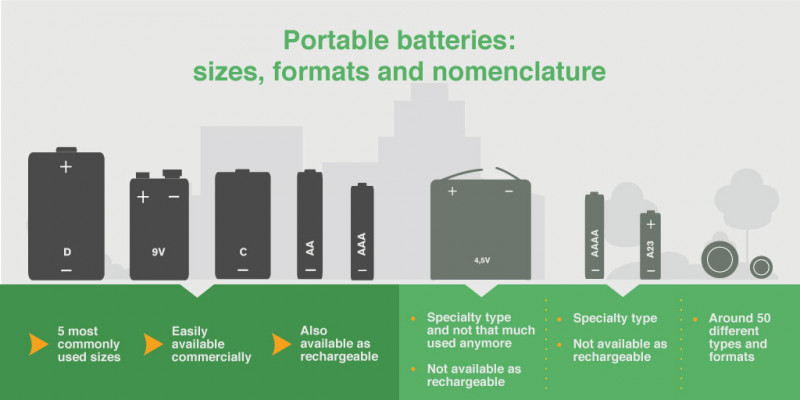
Portable batteries of general use are the standard cylindric or rectangular prism-shaped cells that are commonly found in easily accessible locations such as grocery stores and drugstores. Most are single-use primary batteries, but they can also be rechargeable. Portable batteries of general use are designed to be interoperable and come in one of the following common formats: 4.5 volts (3R12), button cell, D, C, AA, AAA, AAAA, A23, and 9 volts (PP3).
Button cells are typically non-rechargeable and specifically designed for small appliances like hearing aids, watches, and toys. They are shaped like buttons. Rechargeable button cells are also utilized in certain industrial applications.
Battery packs are sets of battery cells or modules that are connected together or encapsulated within an outer casing. They usually contain rechargeable batteries, which fit into the design of appliances such as mobile phones, camcorders, and other portable devices.
Besides these main shapes of batteries, more specialized batteries are made for specific professional users.

EU market for portable batteries
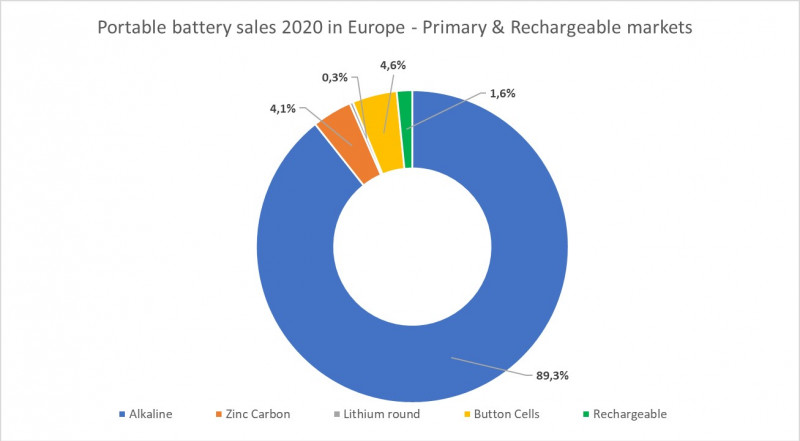
Total primary and rechargeable by volume
According to EPBA statistics, a total of 5.8 billion units of portable batteries were placed on the European market by EPBA members in 2020. This included primary cylindric and prismatic batteries, button cells, and rechargeable batteries and battery packs.
How to choose which portable battery to use?
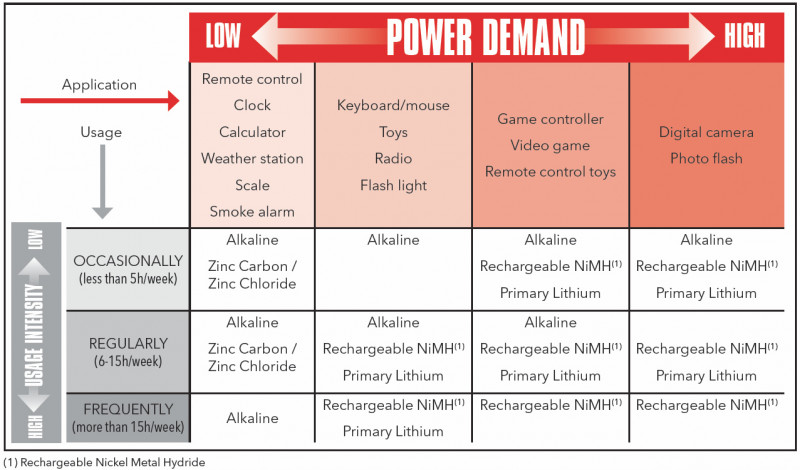
The chemistry of batteries defines the capacity, energy density, and the ability to be recharged. Batteries displaying specific characteristics are then designed for optimal efficiency in specific applications. Portable batteries come in a wide variety of formats, sizes, and chemistries. To ensure the proper functioning of the appliance, efficient energy use, and the safety of the consumer, it is therefore important that the right choices are made when selecting a portable battery to power a device.
Depending on the expected power demand of the appliance and the intensity with which the appliance is used, different portable batteries can be selected - check our selection guide explaining the relation between power demand and frequency of use.
Safe use of portable batteries
Portable batteries are a source of electrical power that can be used in a wide variety of appliances, ranging from remote controls for toys to high-end portable devices. Due to constant product development and innovation, more and more appliances are placed on the market that require a battery to operate. Please follow the general safety guidelines when purchasing and using portable batteries. The guidelines are available here.
